SQL Server JACOBIAN Function
Updated 2024-03-06 17:19:54.580000
Description
Use the scalar function JACOBIAN to numerically compute the Jacobian matrix. The Jacobian matrix is the matrix of all first-order partial derivatives of a vector-valued function.
\textbf{J}\left(\frac{\partial{f}}{\partial{x}_1}\dots\frac{\partial{f}}{\partial{x}_n}\right)=\begin{bmatrix}\frac{\partial{f}_1}{\partial{x}_1}&\dots&\frac{\partial{f}_m}{\partial{x}_n}\\\vdots&\ddots&\vdots\\\frac{\partial{f}_m}{\partial{x}_1}&\dots&\frac{\partial{f}_m}{\partial{x}_n}\end{bmatrix}
Syntax
SELECT [westclintech].[wct].[JACOBIAN] (
<@Func, nvarchar(max),>
,<@VarNames, nvarchar(4000),>
,<@X, nvarchar(4000),>
,<@H, float,>)
Arguments
@Func
The function to be evaluated, as a string. The function must be in the form of a SELECT statement.
@VarNames
The name of the variable.
@X
The point where the Jacobian is calculated.
@H
Step size.
Return Type
nvarchar(max)
Remarks
If Func returns a NULL then NULL Is returned.
If Func is not a valid SELECT statement then NULL is returned.
If no solution is found then NULL is returned.
If @X is NULL then @X = ''.
If @H is NULL then @H = 0.
If H <= 0 then H = 0.000006055
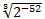
Examples
Example #1
Calculate the Jacobian for the function
f(x,y,z)=\begin{bmatrix}r\sin\theta\cos\varphi\\r\sin\theta\sin\varphi\\r\cos\theta\end{bmatrix}
At the point (2.5, 7/16*π, 63/128*π)
Since the result is returned as a string, we will use the MATRIX function to unpack the results into a matrix format.
DECLARE @r as float = 2.5;
DECLARE @theta as float = 7 * PI() / 16;
DECLARE @phi as float = 63 * PI() / 128;
DECLARE @func as varchar(max)
= '
SELECT
@r*SIN(@theta)*COS(@Phi) as x
,@r*SIN(@theta)*SIN(@Phi) as y
,@r*COS(@theta) as z';
DECLARE @varnames as varchar(max) = '@r,@theta,@phi';
DECLARE @X as varchar(max) = wct.MATRIX2STRING_q('SELECT 2.5, 7*PI()/16,63*PI()
/128');
DECLARE @h as float = wct.POWER(2, -20);
SELECT *
FROM wct.MATRIX(wct.JACOBIAN(@func, @varnames, @X, @h));
This produces the following result.
{"columns":[{"field":"RowNum","headerClass":"ag-right-aligned-header","cellClass":"ag-right-aligned-cell"},{"field":"ColNum","headerClass":"ag-right-aligned-header","cellClass":"ag-right-aligned-cell"},{"field":"ItemValue","headerClass":"ag-right-aligned-header","cellClass":"ag-right-aligned-cell"}],"rows":[{"RowNum":"0","ColNum":"0","ItemValue":"0.0240696757937258"},{"RowNum":"0","ColNum":"1","ItemValue":"0.0119693904816813"},{"RowNum":"0","ColNum":"2","ItemValue":"-2.45122472466392"},{"RowNum":"1","ColNum":"0","ItemValue":"0.980489890091121"},{"RowNum":"1","ColNum":"1","ItemValue":"0.487578913103789"},{"RowNum":"1","ColNum":"2","ItemValue":"0.0601741895079613"},{"RowNum":"2","ColNum":"0","ItemValue":"0.195090322726173"},{"RowNum":"2","ColNum":"1","ItemValue":"-2.45196321015828"},{"RowNum":"2","ColNum":"2","ItemValue":"0"}]}
See Also
HESSIAN - Numerically computer the Hessian matrix
NEWTON - Find the root of a univariate function
SECANT - Find the root of single-variable continuous function.
BRENT - Find the root of a continuous function of on variable