SQL Server RANDBETA Function
Updated 2023-10-18 15:29:15.583000
Description
Use the table-valued function RANDBETA to generate q sequence of random numbers from the beta distribution with two positive shape parameters @a and @b.
Syntax
SELECT * FROM [westclintech].[wct].[RANDBETA](
<@Rows, int,>
,<@a, float,>
,<@b, float,>)
Arguments
@Rows
the number of rows to generate. @Rows must be of the type int or of a type that implicitly converts to int.
@a
the first shape parameter. @a must be of the type float or of a type that implicitly converts to float.
@b
the second shape parameter. @b must be of the type float or of a type that implicitly converts to float.
Return Type
table
{"columns": [{"field": "colName", "headerName": "Name", "header": "name"}, {"field": "colDatatype", "headerName": "Type", "header": "type"}, {"field": "colDesc", "headerName": "Description", "header": "description", "minWidth": 1000}], "rows": [{"id": "ea943357-396f-44ff-a453-f00a51e3f14e", "colName": "Seq", "colDatatype": "int", "colDesc": "A monotonically increasing sequence number"}, {"id": "2bc66060-0ce2-4ae7-b54f-916d3a5d292e", "colName": "X", "colDatatype": "float", "colDesc": "The random variable"}]}
Remarks
@a must be greater than zero.
@b must be greater than zero.
If @a is NULL then @a is set to 1.
If @b is NULL then @b is set to 1.
If @Rows is less than 1 then no rows are returned.
Examples
In this example we create a sequence 1,000,000 random numbers rounded to two decimal places from a beta distribution with @a = 0.5 and @b = 0.5, COUNT the result, paste them into Excel and graph them.
SELECT X,
COUNT(*) as [COUNT]
FROM
(
SELECT ROUND(x, 2) as X
FROM wct.RANDBETA( 1000000, --@Rows
0.5, --@a
0.5 --@b
)
) n
GROUP BY X
ORDER BY 1;
This produces the following result.
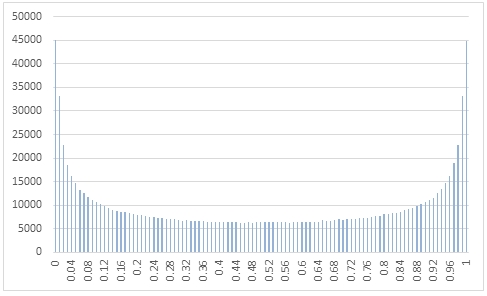
In this example we generate 1,000,000 random numbers from a beta distribution with @a of 2 and @b of 5. We calculate the mean, standard deviation, skewness, and excess kurtosis from the resultant table and compare those values to the expected values for the distribution.
DECLARE @size as int = 1000000;
DECLARE @a as float = 2;
DECLARE @b as float = 5;
DECLARE @mean as float = @a / (@a + @b);
DECLARE @var as float = (@a * @b) / (POWER(@a + @b, 2) * (@a + @b + 1));
DECLARE @stdev as float = SQRT(@var);
DECLARE @skew as float = (2 * (@b - @a) * SQRT(@a + @b + 1)) / ((@a + @b + 2) *
SQRT(@a * @b));
DECLARE @kurt as float
= (6 * (POWER(@a - @b, 2) * (@a + @b + 1) - @a * @b * (@a + @b + 2))) / (@a *
@b * (@a + @b + 2) * (@a + @b + 3));
SELECT stat,
[RANDBETA],
[EXPECTED]
FROM
(
SELECT x.*
FROM
(
SELECT AVG(x) as mean_BETA,
STDEVP(x) as stdev_BETA,
wct.SKEWNESS_P(x) as skew_BETA,
wct.KURTOSIS_P(x) as kurt_BETA
FROM wct.RANDBETA(@size, @a, @b)
) n
CROSS APPLY
(
VALUES
('RANDBETA', 'avg', mean_BETA),
('RANDBETA', 'stdev', stdev_BETA),
('RANDBETA', 'skew', skew_BETA),
('RANDBETA', 'kurt', kurt_BETA),
('EXPECTED', 'avg', @mean),
('EXPECTED', 'stdev', @stdev),
('EXPECTED', 'skew', @skew),
('EXPECTED', 'kurt', @kurt)
) x (fn_name, stat, val_stat)
) d
PIVOT
(
sum(val_stat)
FOR fn_name in ([RANDBETA], [EXPECTED])
) P;
This produces the following result (your result will be different).
{"columns":[{"field":"stat"},{"field":"RANDBETA","headerClass":"ag-right-aligned-header","cellClass":"ag-right-aligned-cell"},{"field":"EXPECTED","headerClass":"ag-right-aligned-header","cellClass":"ag-right-aligned-cell"}],"rows":[{"stat":"avg","RANDBETA":"0.28577495782875","EXPECTED":"0.285714285714286"},{"stat":"kurt","RANDBETA":"-0.119163723672499","EXPECTED":"-0.12"},{"stat":"skew","RANDBETA":"0.597784901594543","EXPECTED":"0.596284793999944"},{"stat":"stdev","RANDBETA":"0.159684726349007","EXPECTED":"0.159719141249985"}]}
See Also
BETAINV - Inverse of the beta distribution
RANDBINOM - Random numbers from a binomial distribution
RANDCAUCHY - Random numbers from a Cauchy distribution
RANDCHISQ - Random numbers from a chi-squared distribution
RANDEXP - Random numbers from an exponential distribution
RANDFDIST - Random numbers from an F-distribution
RANDGAMMA - Random numbers from a gamma distribution
RANDLAPLACE - Random numbers from a LaPlace distribution
RANDLOGISTIC - Random numbers from a logistic distribution
RANDNORMAL - Random numbers from the normal distribution
RANDPOISSON - Random numbers from a Poisson distribution
RANDSNORMAL - Random numbers from the standard normal distribution